Introductory Statistics Book app
free Introductory Statistics Book app
download Introductory Statistics Book app
Introductory Statistics Book apk
free Introductory Statistics Book apk
download Introductory Statistics Book apk

Introductory Statistics Book
4.0
50K+
About This app
Introductory Statistics TextBook by OpenStax plus MCQ, Essay Questions & Key Terms
Introductory Statistics follows scope and sequence requirements of a one-semester introduction to statistics course and is geared toward students majoring in fields other than math or engineering. The text assumes some knowledge of intermediate algebra and focuses on statistics application over theory. Introductory Statistics includes innovative practical applications that make the text relevant and accessible, as well as collaborative exercises, technology integration problems, and statistics labs.
* Complete Textbook by OpenStax
* Multiple Choices Questions (MCQ)
* Essay Questions Flash Cards
* Key-Terms Flash Cards
Powered by https://www.jobilize.com/
1. Sampling and Data
1.1. Definitions of Statistics, Probability, and Key Terms
1.2. Data, Sampling, and Variation in Data and Sampling
1.3. Frequency, Frequency Tables, and Levels of Measurement
1.4. Experimental Design and Ethics
1.5. Data Collection Experiment
1.6. Sampling Experiment
2. Descriptive Statistics
2.1. Stem-and-Leaf Graphs (Stemplots), Line Graphs, and Bar Graphs
2.2. Histograms, Frequency Polygons, and Time Series Graphs
2.3. Measures of the Location of the Data
2.4. Box Plots
2.5. Measures of the Center of the Data
2.6. Skewness and the Mean, Median, and Mode
2.7. Measures of the Spread of the Data
2.8. Descriptive Statistics
3. Probability Topics
3.2. Independent and Mutually Exclusive Events
3.3. Two Basic Rules of Probability
3.4. Contingency Tables
3.5. Tree and Venn Diagrams
3.6. Probability Topics
4. Discrete Random Variables
4.1. Probability Distribution Function (PDF) for a Discrete Random Variable
4.2. Mean or Expected Value and Standard Deviation
4.3. Binomial Distribution
4.4. Geometric Distribution
4.5. Hypergeometric Distribution
4.6. Poisson Distribution
4.7. Discrete Distribution (Playing Card Experiment)
4.8. Discrete Distribution (Lucky Dice Experiment)
5. Continuous Random Variables
5.1. Continuous Probability Functions
5.2. The Uniform Distribution
5.3. The Exponential Distribution
5.4. Continuous Distribution
6. The Normal Distribution
6.1. The Standard Normal Distribution
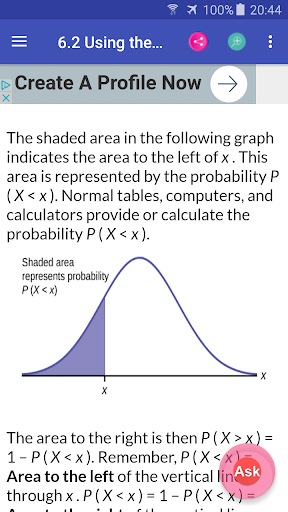
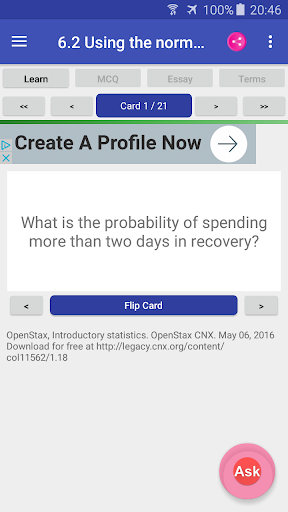
6.2. Using the Normal Distribution
6.3. Normal Distribution (Lap Times)
6.4. Normal Distribution (Pinkie Length)
7. The Central Limit Theorem
7.1. The Central Limit Theorem for Sample Means (Averages)
7.2. The Central Limit Theorem for Sums
7.3. Using the Central Limit Theorem
8. Confidence Intervals
8.1. A Single Population Mean using the Normal Distribution
8.2. A Single Population Mean using the Student t Distribution
8.3. A Population Proportion
9. Hypothesis Testing with One Sample
9.1. Null and Alternative Hypotheses
9.2. Outcomes and the Type I and Type II Errors
9.3. Distribution Needed for Hypothesis Testing
9.4. Rare Events, the Sample, Decision and Conclusion
9.5. Additional Information and Full Hypothesis Test Examples
9.6. Hypothesis Testing of a Single Mean and Single Proportion
10. Hypothesis Testing with Two Samples
10.1. Two Population Means with Unknown Standard Deviations
10.2. Two Population Means with Known Standard Deviations
10.3. Comparing Two Independent Population Proportions
10.4. Matched or Paired Samples
10.5. Hypothesis Testing for Two Means and Two Proportions
11. The Chi-Square Distribution
11.2. Goodness-of-Fit Test
11.3. Test of Independence
11.4. Test for Homogeneity
11.6. Test of a Single Variance
12. Linear Regression and Correlation
12.1. Linear Equations
12.2. Scatter Plots
12.3. The Regression Equation
12.4. Testing the Significance of the Correlation Coefficient
12.5. Prediction
12.6. Outliers
12.7. Regression (Distance from School)
12.8. Regression (Textbook Cost)
12.9. Regression (Fuel Efficiency)
13. F Distribution and One-Way ANOVA
Show More
Screenshots
Comment
Similar Apps
Top Downloads
Copy [email protected]. All Rights Reserved
Google Play™ is a Trademark of Google Inc.
ApkYes is not affiliated with Google, Android OEMs or Android application developers in any way.